Experiencing hair loss due to medication can be frustrating, especially when you’re already managing other health challenges. It’s crucial to understand why this happens and how medications affect your hair follicles, so you can take proactive steps to minimize hair loss and encourage regrowth.

💊 How Medications Affect Hair Growth
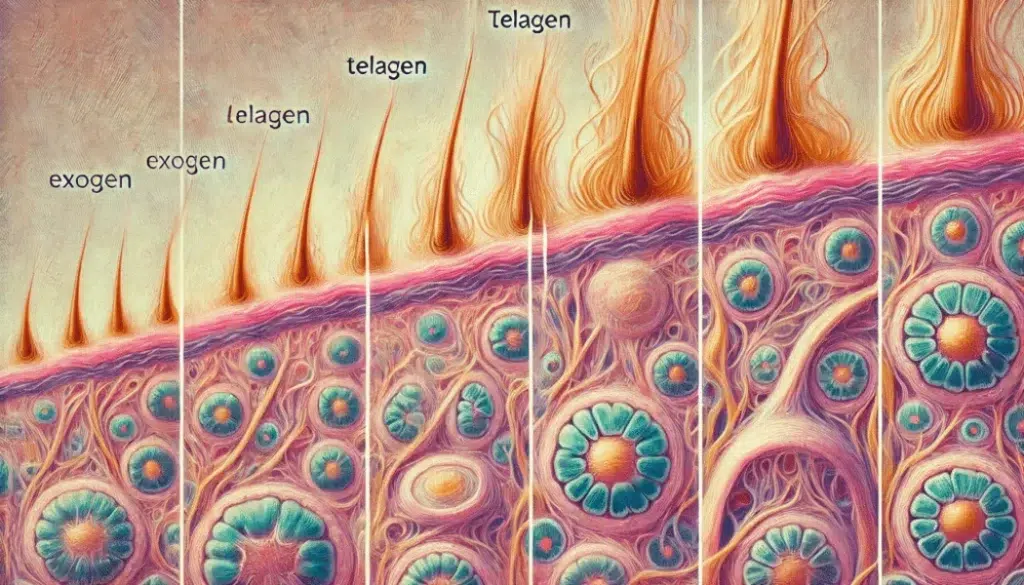
Medications can interfere with the natural cycle of hair growth, which consists of a growth phase (anagen), a resting phase (telogen), and a shedding phase (exogen). Some medications prematurely push hair follicles into the shedding phase or extend the resting phase, leading to noticeable thinning or loss.
In addition, some medications cause nutrient deficiencies, which weaken the hair structure over time. Others create hormonal imbalances, disrupting the balance of testosterone, estrogen, and thyroid hormones, all of which play a role in healthy hair growth. Medications that reduce blood circulation to the scalp can also contribute to hair thinning by depriving follicles of essential nutrients and oxygen.
🧾 Medications That Can Trigger Hair Loss
Various types of medications can lead to hair loss, including:
- Chemotherapy drugs: These aggressively target rapidly dividing cells, including hair follicles, leading to extensive hair loss, often across the entire scalp and body.
- Beta-blockers: Used to manage heart conditions and blood pressure, but they may interfere with the normal hair growth cycle and cause thinning.
- Antidepressants and mood stabilizers: Certain selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and mood stabilizers have been linked to increased hair shedding.
- Hormone therapies: Birth control pills, hormone replacement therapy, and thyroid medications can disrupt hormonal balance, impacting hair density.
- Retinoids and acne medications: High doses of vitamin A or isotretinoin (Accutane) may cause hair to become brittle and shed at a faster rate.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs and steroids): Long-term use of these medications may weaken hair follicles, leading to noticeable thinning.
- Anticoagulants (blood thinners): Some blood-thinning medications have been linked to increased hair shedding by affecting follicular health.

Now that we understand how medications can affect hair growth, let’s take a closer look at specific types of drugs that are commonly associated with hair loss
⏳ Is Hair Loss from Medication Temporary?
Medication-induced hair loss is often temporary, but its duration depends on several factors:
- If hair loss occurs due to short-term medication use, regrowth typically starts within a few months after discontinuing treatment.
- Long-term use of certain medications may require more time for regrowth and additional treatments.
- Some medications, particularly those affecting hormonal balance or immune response, may cause permanent follicle damage, making hair loss irreversible in severe cases.
In most cases, once the medication is adjusted or stopped, hair follicles recover, and new growth resumes within 3 to 6 months. However, extra hair care and support can accelerate this process.
🔍 Is Your Medication Causing Hair Loss?
To determine whether your medication is causing hair loss, consider the following:
- Timing of hair loss: Did excessive shedding begin after starting or increasing a specific medication?
- Pattern of hair loss: Is thinning widespread, or is it focused on particular areas such as the temples or crown?
- Additional symptoms: Have you noticed changes in hair texture, brittleness, or excessive dryness?
Maintaining a hair diary can help track changes and provide useful insights when discussing concerns with your healthcare provider. Never stop taking medication without consulting your doctor, as they may recommend dosage adjustments or alternative treatments.
🛡️ How to Protect Your Hair While on Medication
Taking proactive steps can help minimize medication-induced hair loss:
- Nourish Your Hair with Proper Nutrition: Ensure your diet includes essential vitamins such as biotin, iron, zinc, and Omega-3 fatty acids. Foods like eggs, nuts, leafy greens, and fish can strengthen hair follicles and promote regrowth.
- Scalp Care and Stimulation: Use gentle, sulfate-free shampoos and massage your scalp regularly to increase blood circulation to the hair follicles.
- Manage Stress Levels: Chronic stress exacerbates hair loss. Incorporate yoga, meditation, deep breathing, or regular walks to reduce cortisol levels. Additional use of supplements against accumulated stress could effectively reduce scalp problems.
- Minimize Heat and Chemical Damage: Avoid excessive heat styling, hair dyes, and chemical treatments that weaken hair strands and accelerate breakage.
- Stay Hydrated and Exercise Regularly: Good hydration and moderate physical activity improve circulation, supporting stronger, healthier hair growth.
- Use Essential Oils: Rosemary, peppermint, and castor oil are known to improve scalp health and stimulate growth.
- Protect Hair at Night: Using a silk pillowcase reduces friction and prevents breakage.

By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, balanced nutrition, and gentle hair care routine, you can provide the best conditions for hair preservation and regrowth.
🌿 Hair Care Alternatives and Solutions
If medication-induced hair loss persists, explore these solutions:
- Consult Your Doctor: Consult your doctor about possible alternative medications with a lower risk of hair loss. They may suggest adjusting your dosage or switching to a different prescription.
- Consider Minoxidil: This FDA-approved topical treatment may stimulate regrowth and slow further thinning. In addition to minoxidil, these lotions contain natural ingredients that block harmful DHT (dihydrotestosterone derivative) and other natural ingredients that improve the health of your scalp.
- Consider Hair Growth Supplements: Certain formulas, such as those containing field horsetail extract, nettle, and L-cysteine, may support hair health and regrowth
- Explore Natural Remedies: Scalp massages with special lotions that strongly and proven improve the health of the scalp and promote hair growth
- Professional Treatments: Consult a dermatologist or trichologist about low-level laser therapy (LLLT), which is proven to be effective, widely available, easy to use, and safe for your health.
- Hair Transplantation (in severe cases): If hair loss is significant and persistent, a hair transplant procedure may be an option.

🔄 Lifestyle Changes to Support Hair Health
Beyond medications, other lifestyle habits can exacerbate hair thinning. To further protect your hair:
- Reduce smoking and alcohol consumption, as these negatively impact circulation and follicle health.
- Use silk pillowcases to reduce hair breakage while sleeping.
- Protect your hair from harsh weather conditions, such as excessive sun exposure or cold air.
- Increase Protein Intake: Hair is made primarily of keratin, a type of protein, so eating more protein-rich foods can strengthen hair.

🧭 Wrapping Up: What to Keep in Mind
Medication-induced hair loss can be temporary or manageable, depending on the underlying cause and how quickly proactive measures are taken. By identifying potential triggers, adjusting lifestyle habits, and seeking medical advice, you can effectively minimize hair loss and encourage healthy regrowth.
If you’re struggling with hair loss due to medication, take proactive steps today. Consult with a professional, adjust your hair care routine, and explore treatments that work best for you. Have you experienced medication-related hair loss? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
Stay with us — the best is yet to come.
By following our advice, you’re doing the most you can for your hair.
Be the first to know when we publish new guides, tests, and proven strategies for stronger, healthier hair.
👉 Visit the About Me page to learn more about my journey, mission, and why helping people with hair health is so personal to me.
Want healthier, stronger hair? Discover 8 science-backed habits that protect your scalp and boost natural growth. Get your free PDF guide today!
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Sensitive claims are supported with scientific references, and full product details can always be found on the official websites of the respective manufacturers or distributors.
Some links in this article are affiliate links. If you choose to make a purchase through them, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you — helping me keep HairGrowGenius running. Thank you for your support!

✅ FAQ – How to Prevent Hair Loss While on Medication
❓ Which types of medications are most commonly linked to hair loss?
Common culprits include beta-blockers, antidepressants, anticonvulsants, acne treatments like isotretinoin, and chemotherapy agents. Some hormone-based drugs (like birth control or testosterone therapy) can also trigger hair shedding in sensitive individuals.
❓ Is drug-induced hair loss always permanent?
Not usually. In most cases, hair loss is temporary and resolves once the medication is discontinued or replaced. However, long-term use or underlying health conditions can sometimes prolong or worsen the shedding phase.
❓ Can I take supplements to offset medication-related hair loss?
Yes—nutrients like biotin, zinc, B-complex vitamins, and iron may support hair health during treatment. However, always check with your doctor first to avoid interactions, especially if you’re on blood thinners or hormonal medications.
❓ Should I stop taking a medication if it causes hair loss?
Never stop a prescribed medication without medical supervision. Talk to your doctor—there may be alternative drugs with less impact on hair, or strategies to manage the side effect without risking your overall health.
Last updated: June 2025 based on latest research


Leave a Reply