Thyroid hormones might sound like some complicated science, but they play a crucial role in keeping our bodies ticking along smoothly. T3, known as triiodothyronine, and T4, or thyroxine, are the main hormones produced by the thyroid gland. Think of them as the dynamic duo controlling the pace at which your body uses energy and produces proteins. They’re like silent managers, overseeing various bodily functions without most of us even noticing.
T3 and T4 regulate metabolism, which is essential for keeping our energy levels on point. They influence how our body breaks down food, manages body temperature, and even affects how our cells interact. Imagine these hormones as the battery power behind your favorite gadget – unnoticed until they’re not working right, then suddenly everything’s out of whack.
Ever had those days when you’re just not feeling right? It could be your thyroid acting up. When T3 and T4 are balanced, everything runs smooth. But too much or too little can lead to symptoms like fatigue, weight fluctuation, and yes, hair loss. Keeping these hormones in check is key to feeling good and looking healthy. Our bodies really do need them to function at their best.
🧠 The Thyroid-Hair Connection: How Hormones Affect Hair Growth
Hair may seem like an afterthought, but its growth and maintenance are all part of a complex cycle driven by various factors, including thyroid hormones. Understanding this cycle is essential to recognizing what goes wrong when hair loss occurs.
The hair growth cycle is broken down into three phases: anagen, catagen, and telogen. Anagen is the growth phase where new hair is formed. Catagen is a short transitional phase, and telogen is the rest phase, where older hairs are shed. Thyroid hormones play a significant role in regulating the length and health of each cycle, specifically keeping the anagen phase active and vigorous.
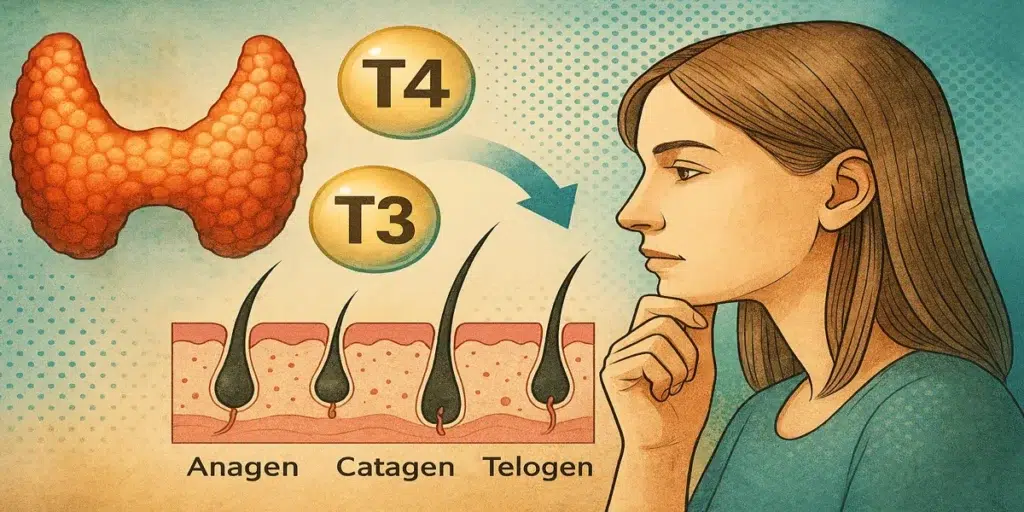
When our thyroid hormones are imbalanced, it can disrupt this cycle, slowing down the growth phase or speeding up the resting phase. This imbalance often leads to hair becoming thinner, more brittle, and falling out more than usual. It’s a bit like running on a treadmill that suddenly goes haywire, either speeding up or slowing down unpredictably, causing a stumble or fall.
A well-functioning thyroid supports the follicle metabolism, ensuring that energy and nutrients are adequately supplied to hair follicles. When there’s a deficiency or excess of thyroid hormones, the metabolism of these follicles is disrupted, causing stress and leading to weak or lifeless hair. This hormonal hiccup can create a noticeable difference in the appearance and texture of hair.
Being aware of how critical thyroid hormones are to the hair cycle helps in understanding why monitoring and maintaining balanced hormone levels is vital. If you’ve noticed sudden changes in your hair’s health or appearance, it might just be a sign to check in on those hormone levels. Recognizing this connection is the first step in addressing potential issues.
⚖️ Hypothyroidism vs. Hyperthyroidism: Unraveling Their Impact on Hair
When it comes to thyroid issues, hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are like two sides of a complicated coin, each affecting hair in distinct ways. Knowing the difference between these conditions is vital for understanding why your luscious locks may be losing their luster.
Hypothyroidism occurs when your thyroid isn’t producing enough hormones. This can slow down many body processes, including hair growth. The result? Hair that’s dry, brittle, and breaking more easily. Imagine trying to grow a garden with not enough sunlight and water; things just don’t thrive.

On the flip side is hyperthyroidism, where the thyroid is a little too productive, pumping out hormones at an overactive pace. This leads to the opposite problem: thinning hair due to rapid metabolism and quicker-than-normal hair cycle progression. Your follicles can’t keep up with the sped-up demands, leading to noticeable thinning, especially across the scalp.
Both conditions can also lead to what’s known as ‘diffuse thinning.’ Unlike pattern baldness, which is localized, diffuse thinning affects your whole scalp, making it look less dense. It’s often one of the first signs something’s amiss endocrinologically speaking.
Identifying whether it’s hypo- or hyperthyroidism causing hair woes requires a bit more than just examination. Tests like blood panels are essential in pinpointing these conditions accurately. Understanding the specific cause of hair loss helps in targeting the right treatments and managing expectations effectively.
🔍 Recognizing and Diagnosing Thyroid-Related Hair Loss
Spotting when hair loss is thyroid-related can feel a bit like solving a mystery. The signs are there, but it takes a keen eye to piece them together. Hair loss linked to thyroid issues isn’t just about what’s on your head. It’s part of a bigger picture involving other body symptoms.
Thyroid-related hair loss often goes hand-in-hand with symptoms like fatigue, unexplained weight changes, and even mood swings. If you notice your hairbrush gathering more strands than usual and you’re feeling perpetually tired or experiencing dramatic weight shifts, it’s worth considering that your thyroid might be playing a part.
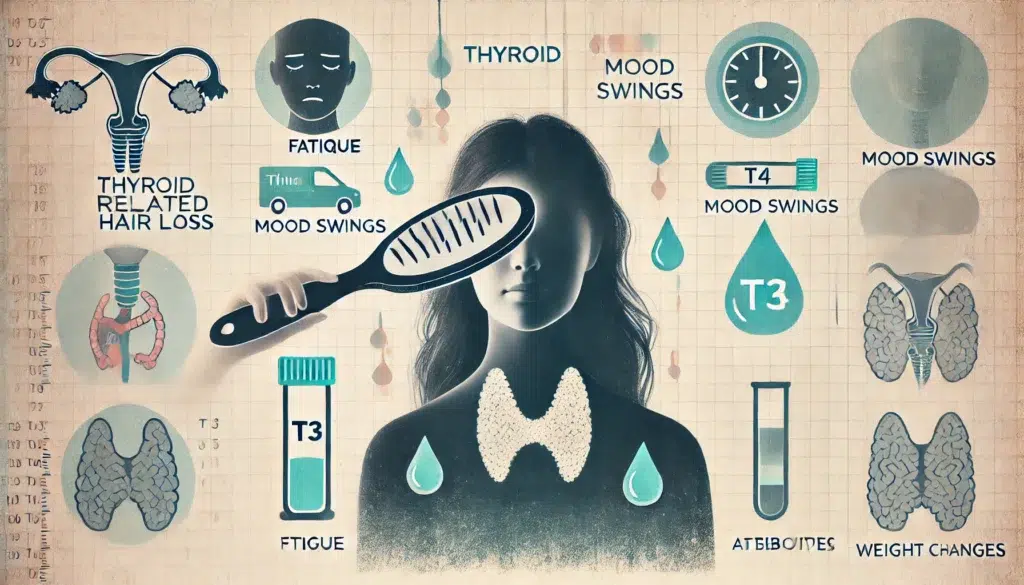

To get a clear diagnosis, comprehensive blood tests are usually the way to go. Tests measuring Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH), Free T3, Free T4, and thyroid antibodies provide a window into thyroid health. These tests not only confirm whether the thyroid gland’s output is off-kilter but also help differentiate between various thyroid-related conditions.
It’s crucial to differentiate between thyroid-related hair loss and other potential causes, such as nutritional deficiencies or stress. Consulting with a healthcare provider who can guide you through the appropriate tests based on your symptoms is always a good bet.
Understanding these connections and acting when something feels amiss is important for both comfort and health. Getting to the root of the problem with a medical professional’s help allows not just hair recovery, but overall well-being.
🛠️ Reversing and Treating Hair Loss: Effective Strategies and Treatments
Experiencing hair loss due to thyroid issues can be distressing, but the good news is there are ways to manage and even reverse it. The main focus is on addressing the thyroid imbalance that causes it. Restoring hormone levels to their ideal range is the foundation for treatment. Once your thyroid is balanced out, many people notice their hair starting to bounce back over time.
Thyroid medications, particularly those prescribed for hypo- or hyperthyroidism, often play a crucial role here. By stabilizing hormone production through medications like levothyroxine for hypothyroidism or antithyroid drugs for hyperthyroidism, you’re addressing the root problem rather than just the symptoms.

Alongside medical treatments, there are additional approaches to support hair regrowth. Nutritional supplements such as biotin, zinc, and selenium are often recommended to boost hair health. But, it’s important to tread carefully with these, and not use them indiscriminately, as excessive amounts can sometimes complicate thyroid issues further.
Sometimes lifestyle tweaks offer added benefits. Eating a balanced diet, managing stress, and avoiding harsh hair treatments can create a supportive environment for hair recovery. However, these are supplementary steps and should ideally be combined with medical interventions for the best results.
If hair loss persists despite these efforts, it’s wise to seek further advice from a healthcare provider or endocrinologist. They can explore other potential underlying causes or reevaluate treatment approaches, ensuring your hair recovery is on the right track.
Stay with us — the best is yet to come.
By following our advice, you’re doing the most you can for your hair.
Be the first to know when we publish new guides, tests, and proven strategies for stronger, healthier hair.
👉 Visit the About Me page to learn more about my journey, mission, and why helping people with hair health is so personal to me.
Want healthier, stronger hair? Discover 8 science-backed habits that protect your scalp and boost natural growth. Get your free PDF guide today!
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Sensitive claims are supported with scientific references, and full product details can always be found on the official websites of the respective manufacturers or distributors.
Some links in this article are affiliate links. If you choose to make a purchase through them, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you — helping me keep HairGrowGenius running. Thank you for your support!

✅ FAQ – The Impact of Thyroid Hormones on Hair Loss
❓ Can hair loss from thyroid imbalance be the first sign of a thyroid disorder?
Yes. In many cases, hair thinning or unusual shedding may appear before other symptoms like fatigue, weight changes, or mood swings. If your hair loss is sudden and diffuse, especially alongside brittle nails or dry skin, thyroid testing is a smart next step.
❓ Is thyroid-related hair loss more common with hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism?
Both can cause hair loss, but it’s more commonly associated with hypothyroidism, where the slowdown in metabolism weakens hair follicles and shortens the growth phase. However, hyperthyroidism can also lead to thinning due to hormonal imbalance and nutrient depletion.
❓ Does hair regrow after treating thyroid imbalance?
Often yes—but it takes time. Once thyroid hormone levels are stabilized through medication or lifestyle changes, hair usually begins to recover after 3–6 months. Full regrowth can take up to a year, depending on how long the imbalance persisted.
❓ What nutrients support hair regrowth in people with thyroid disorders?
Key nutrients include selenium, zinc, biotin, vitamin D, and iron—all vital for healthy hair growth and proper thyroid function. Supporting your thyroid nutritionally often supports your scalp as well.
Last updated: June 2025 based on latest research


Leave a Reply